Understanding Enteric Fever: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Enteric fever, commonly known as typhoid fever, is a bacterial infection caused by the Salmonella typhi bacteria. This disease poses a significant public health challenge, especially in regions with poor sanitation and hygiene practices. Let’s delve deeper into enteric fever to understand its causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention methods.
Causes
Enteric fever is primarily caused by the bacterium Salmonella typhi. This bacterium resides in the intestines and bloodstream of infected individuals and is shed in feces. The contamination of food and water sources with fecal matter containing the bacteria is the primary mode of transmission. Factors such as poor sanitation, inadequate sewage disposal, and lack of access to clean water contribute to the spread of this disease.
Symptoms
The symptoms of enteric fever usually develop 1-3 weeks after exposure to the bacteria. Common symptoms include:
- Fever: Persistent high fever, often ranging from 103-104°F (39-40°C).
- Headache and Body Aches: Generalized headaches and muscle pains, accompanied by weakness and fatigue.
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Abdominal pain, diarrhea (more common in the early stages), or constipation.
- Rose Spots: Small, pink, flat spots on the trunk and abdomen, although not always present.
- Other Symptoms: Dry cough, enlarged spleen and liver, and confusion in severe cases.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of enteric fever involves clinical evaluation, travel history assessment, and laboratory tests. Blood cultures and stool cultures are commonly conducted to isolate and identify the Salmonella typhi bacteria, confirming the diagnosis.
Typhoid Test Using Rapid Typhidot Card
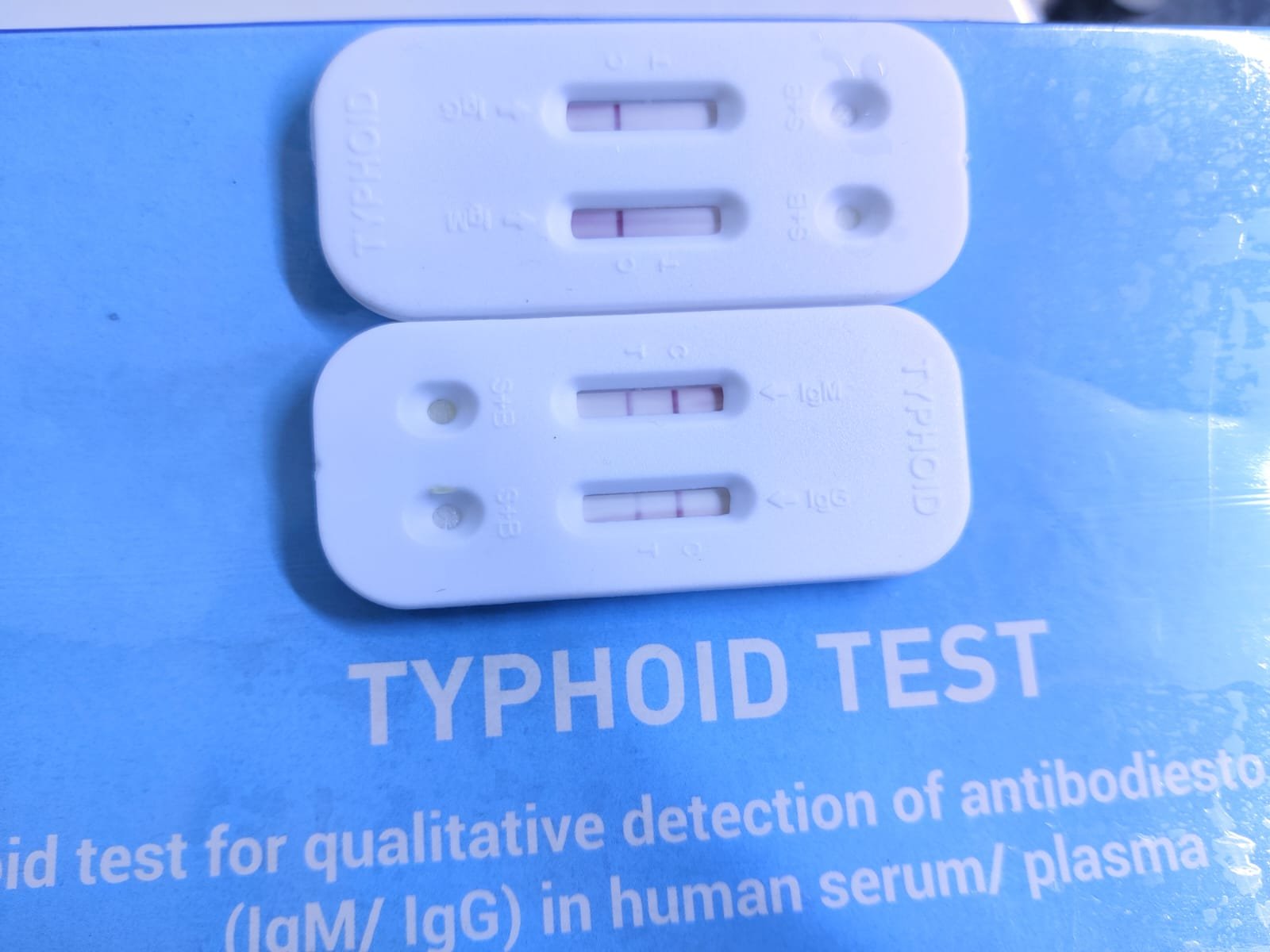
The rapid Typhidot test is a convenient and quick diagnostic tool used to detect antibodies against Salmonella typhi, the bacteria responsible for causing typhoid fever. This test provides rapid results, usually within 2-3 minutes, making it invaluable for timely diagnosis and treatment initiation. Here’s a detailed overview of the Typhidot test and its utility in diagnosing typhoid fever.
Treatment
Treatment of enteric fever focuses on eliminating the bacteria with antibiotics. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins, and azithromycin. The duration of treatment is typically 7-14 days but may extend longer for complicated cases or suspected antibiotic resistance. Adequate hydration and supportive care are also crucial aspects of treatment.
Prevention
Prevention is key to controlling the spread of enteric fever. Here are some preventive measures:
- Vaccination: Vaccines against typhoid fever are available and recommended for travelers visiting endemic regions and individuals at high risk of exposure.
- Good Hygiene: Practicing regular handwashing with soap and water can help prevent the spread of the disease.
- Safe Food and Water: Consuming properly cooked food and safe, clean water is vital. Avoiding raw or undercooked foods and beverages made with untreated water can reduce the risk of contamination.
Conclusion
Enteric fever remains a significant public health concern globally, especially in regions with inadequate sanitation infrastructure. Efforts to improve sanitation, access to clean water, and vaccination coverage are crucial for controlling the spread of this disease and reducing its impact on communities. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms early, seeking timely medical care, and adopting preventive measures, we can combat enteric fever and protect our communities from this infectious disease.